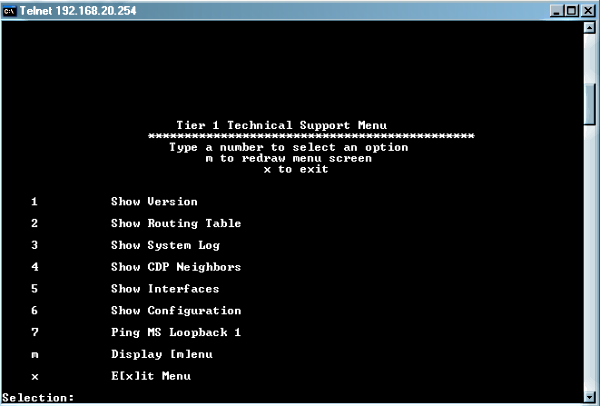
The Interview
I´ve been working in Networking/Security Field for a while and most of my interviews didn´t have a deep technical session like my last one. A friend of mine (André) suggested me to apply for a Technical Consultant Role like him did last year, and after talk with him about his projets i decided to go … Read more